Nov 3, 1777:
Washington learns of Conway cabal
On this day in 1777, General George Washington is informed that a conspiracy is afoot to discredit him with Congress and have him replaced by General Horatio Gates. Thomas Conway, who would be made inspector general of the United States less than two months later on December 14, led the effort.
Conway, who was born in Ireland but raised in France, entered the French army in 1749. He was recruited to the Patriot cause by Silas Deane, the American ambassador to France, and after meeting with Washington at Morristown in May 1777, he was appointed brigadier general and assigned to Major General John Sullivan's division.
Conway served admirably under Sullivan at the battles of Brandywine, in September 1777, and Germantown, in October 1777, before becoming involved in an unconfirmed conspiracy to remove General Washington from command of the Continental Army. The rumored conspiracy would go down in history as the "Conway cabal."
After the Continental Army suffered several defeats in the fall of 1777, some members of Congress expressed displeasure with Washington's leadership and Conway began writing letters to prominent leaders, including General Horatio Gates, that were critical of Washington. After Washington got wind of Conway's letter to General Gates, he responded with a letter to Congress in January 1778. Embarrassed, Conway offered his resignation in March 1778 by way of apology, and was surprised and humiliated when Congress accepted. After General John Cadwalader wounded him in a duel defending Washington's honor, Conway returned to France, where he died in exile in 1800.
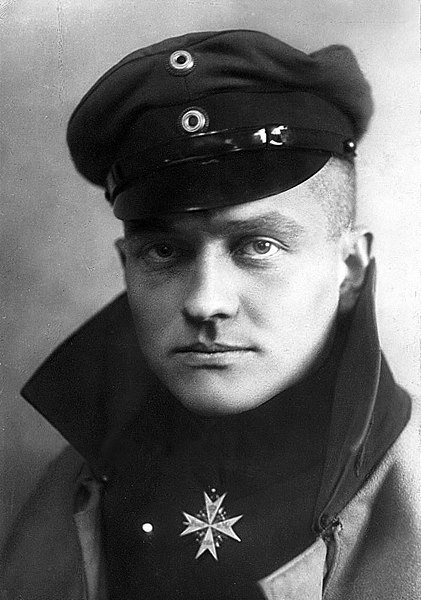
 French-Irish General Thomas Conway, for whom the controversy was named
Nov 3, 1984:
French-Irish General Thomas Conway, for whom the controversy was named
Nov 3, 1984:
A serial killer abducts and rapes his teenage victim
Bobby Joe Long kidnaps and rapes 17-year-old Lisa McVey in Tampa, Florida. The victim's subsequent courage and bravery led to the capture and arrest of Long, who was eventually found guilty of 10 murders committed in the Tampa area during the early 1980s.
McVey had been riding her bicycle home from work in the evening when she was abducted and blindfolded by Long. He then smuggled her into an apartment where he sexually assaulted her for more than a day. While successfully convincing Long to spare her life, McVey remained mentally alert enough throughout the brutal ordeal to remember certain details that were crucial in helping police capture her attacker.
By estimating the amount of time she spent in Long's car after being abducted, McVey was able to help establish a radius for his location. She also was able to estimate the time of day that Long had used an ATM by recalling the television show music she heard playing faintly in the background. Since ATM's were still relatively rare in 1984, police were able to narrow possible culprits by checking out everyone who had conducted an ATM transaction in that time frame and area. Lastly, the victim had seen enough of Long's car to provide details that helped identify its year and model.
With this critical information, police were able to locate and arrest Long on November 16. After confessing to 10 area homicides, he received a string of 99-year prison terms and two death penalty sentences, although the latter were eventually overturned because he had been interrogated despite his requests to speak to a lawyer.
 Nov 3, 1903:
Nov 3, 1903:
Panama declares independence
With the support of the U.S. government, Panama issues a declaration of independence from Colombia. The revolution was engineered by a Panamanian faction backed by the Panama Canal Company, a French-U.S. corporation that hoped to connect the Atlantic and Pacific oceans with a waterway across the Isthmus of Panama.
In 1903, the Hay-Herrán Treaty was signed with Colombia, granting the United States use of the Isthmus of Panama in exchange for financial compensation. The U.S. Senate ratified the treaty, but the Colombian Senate, fearing a loss of sovereignty, refused. In response, President Theodore Roosevelt gave tacit approval to a rebellion by Panamanian nationalists, which began on November 3, 1903. To aid the rebels, the U.S.-administered railroad in Panama removed its trains from the northern terminus of Colón, thus stranding Colombian troops sent to crush the insurrection. Other Colombian forces were discouraged from marching on Panama by the arrival of the U.S. warship Nashville.
On November 6, the United States recognized the Republic of Panama, and on November 18 the Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty was signed with Panama, granting the United States exclusive and permanent possession of the Panama Canal Zone. In exchange, Panama received $10 million and an annuity of $250,000 beginning nine years later. The treaty was negotiated by U.S. Secretary of State John Hay and the owner of the Panama Canal Company. Almost immediately, the treaty was condemned by many Panamanians as an infringement on their country's new national sovereignty.
On August 15, 1914, the Panama Canal was inaugurated with the passage of the U.S. vessel Ancon, a cargo and passenger ship. After decades of protest and negotiations, the Panama Canal passed to Panamanian control in December 1999.
 Nov 3, 1957:
Nov 3, 1957:
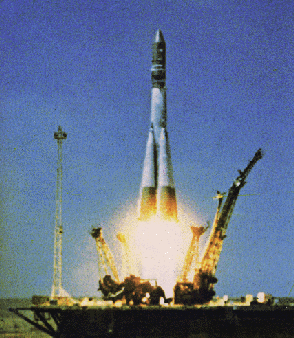
The Soviet space dog
The Soviet Union launches the first animal into space—a dog name Laika—aboard the Sputnik 2 spacecraft.
Laika, part Siberian husky, lived as a stray on the Moscow streets before being enlisted into the Soviet space program. Laika survived for several days as a passenger in the USSR's second artificial Earth satellite, kept alive by a sophisticated life-support system. Electrodes attached to her body provided scientists on the ground with important information about the biological effects of space travel. She died after the batteries of her life-support system ran down.
At least a dozen more Russian dogs were launched into space in preparation for the first manned Soviet space mission, and at least five of these dogs died in flight. On April 12, 1961, Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human to travel into space, aboard the spacecraft Vostok 1. He orbited Earth once before landing safely in the USSR.
 Nov 3, 1962:
Nov 3, 1962:
The Crystals earn a #1 hit with "He's A Rebel"—or do they?
In an incident familiar to all fans of pop music scandals, a great hue and cry was raised in the press and in the music industry when the late 1980s dance sensation Milli Vanilli was exposed as mere lip-sync artists. Suddenly exposed as illegitimate, the duo that had earned a #1 hit with "Baby Don't Forget My Number" (1989) was immediately stripped of its Grammy Award for Best New Artist. But fans of pop music hypocrisy know that the music industry's definitions of "legitimate" and "illegitimate" have always been flexible, and that Milli Vanilli was hardly the first chart-topping act with a scandalous secret. Another such act scored a #1 hit on this day in 1962, in fact, when their name appeared at the top the Billboard Hot 100 alongside the song "He's A Rebel"—a record on which the credited artists, the Crystals, had not sung a single note.
Formed in Brooklyn by five high school classmates, the Crystals were a legitimate vocal group who managed to secure a contract with the newly formed Philles record label in 1961. Philles was under the creative control of the soon-to-be-legendary producer Phil Spector, who took the Crystals under his wing and helped them record two top 20 hits in "There's No Other" (#20, December 1961) and "Uptown" (#13, May 1962). While their third release—the Gerry Goffin-Carole King-penned "He Hit Me (And It Felt Like A Kiss)"—flopped when radio stations rejected it over subject-matter concerns, the next single released under their name would go all the way to #1.
Although few people knew it at the time, however, rightful credit for that record belongs to a group called the Blossoms, whose lead singer, Darlene Love, would earn two minor top 40 hits of her own in 1963 with "(Today I Met) The Boy I'm Gonna Marry" and "Wait Til' My Bobby Gets Home," but who would receive none of the credit for "He's A Rebel." With the Crystals back in New York, Phil Spector chose to record "He's A Rebel" with the Blossoms in Los Angeles in order to get the record out ahead of a competing version by Vicki Carr. Since the Blossoms and Darlene Love were complete unknowns, the record was credited to the Crystals
The Crystals would go on to "earn" one more major hit with a song recorded by Darlene Love and the Blossoms: "He's Sure The Boy I Love" (#11, February 1963). They would also earn even bigger hits, however, with songs they actually did record: "Da Doo Ron Ron (When He Walked Me Home)" (#3, June 1963) and "Then He Kissed Me" (#6, September 1963)







 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote